Introduction
Today, interior design has transcended mere aesthetics to incorporate principles that reflect a greater environmental and wellness awareness. In this context, the terms sustainable, healthy and green design have become fundamental pillars of conscious design. However, despite their growing popularity, the differences between these approaches are not always well understood. In this article, I will break down each of these concepts to understand how they can transform not only our spaces but also our environment and health.
Application of Concepts to Interior Design
The principles of sustainability, health and ecology in interior design are not mutually exclusive, but often overlap and complement each other. Sustainable refers to the ability to create environments that support resource conservation, reducing environmental impact and ensuring that future generations can enjoy the same resources we do today. In terms of design, this translates into choosing recycled or easily renewable materials, as well as building practices that minimize waste.
Healthy design, on the other hand, focuses on creating spaces that promote the physical and mental well-being of their occupants. This includes indoor air quality, ergonomics, natural lighting and minimizing toxins in the materials used. As well as taking care to avoid electromagnetic pollution inside the home.
Finally, a green approach goes beyond sustainability to focus on living in harmony with the environment. This may involve the use of technologies that mimic or preserve natural cycles and systems that reduce carbon emissions and the ecological footprint of buildings.
What is Sustainable Interior Design?
The concept of sustainability in interior design goes beyond simply selecting products labeled "green." It involves a holistic approach that considers every element and process with the goal of minimizing environmental impact throughout the life cycle of a project. Interior sustainability focuses on optimizing resources, extending the life of materials and promoting practices that reduce the ecological footprint.
Definition and Principles of Sustainability in Interiors
Sustainability in the context of interior design is defined as the ability to design and use spaces in a way that ensures the least amount of waste of resources and energy. This includes not only the materials used, but also aspects such as energy efficiency and water management. The fundamental principles of sustainable design include:
- Energy Efficiency: Implementation of systems that reduce energy consumption, such as LED lighting and energy-efficient appliances.
- Indoor Air Quality: Use of materials and finishes that do not emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other toxins.
- Renewable and Recycled Materials: Choice of materials that are recyclable or from sustainable sources, such as certified wood, bamboo and natural textiles.
- Durability and Adaptability: Design spaces that are capable of adapting to different uses over time to avoid frequent renovations and the consequent waste of materials.
Materials and Best Practices
Embracing sustainability in interior design not only benefits the planet, but also the occupants of the space. For example, using paints and finishes without toxic compounds improves indoor air quality, contributing to a healthier environment. Some best practices include:
- Selection of Local Materials: Reduce the carbon footprint associated with the transportation of materials by choosing local suppliers.
- Creative Reuse: Integrating existing elements into new designs, such as recycling old wood for flooring or furniture.
- Green Technology: Incorporate technologies that reduce energy consumption, such as daylight sensors and smart thermostats.
What is Healthy Interior Design?
Health in interior design is not only about avoiding toxic materials, but also about creating environments that promote the physical and mental well-being of users. Healthy interior design integrates elements that improve air quality, optimize natural lighting and minimize the presence of pollutants, all contributing to a more comfortable and psychologically positive environment.
Impact of Interiors on Human Health
The indoor environment of a space can have significant effects on the physical and mental health of those who live in it. Factors such as air quality, lighting and ergonomics not only affect daily well-being, but also have long-term impacts on health. For example, poor indoor air quality has been linked to respiratory illness and reduced productivity, while proper lighting can improve mood and energy efficiency in the home.
Elements Characterizing a Healthy Indoor Space
Creating a healthy space involves several strategic considerations, including:
- Air Quality: Use efficient ventilation systems and low-emission materials to keep the air clean and fresh.
- Natural Lighting: Maximize the use of natural light to reduce dependence on artificial lighting, which benefits circadian rhythm regulation and improves overall mood.
- Non-Toxic Materials: Choose materials such as paints, adhesives and finishes with low or zero levels of volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- Ergonomics: Designing spaces that promote healthy posture and minimize physical stress, which is essential in the workplace or for people with autism syndrome.
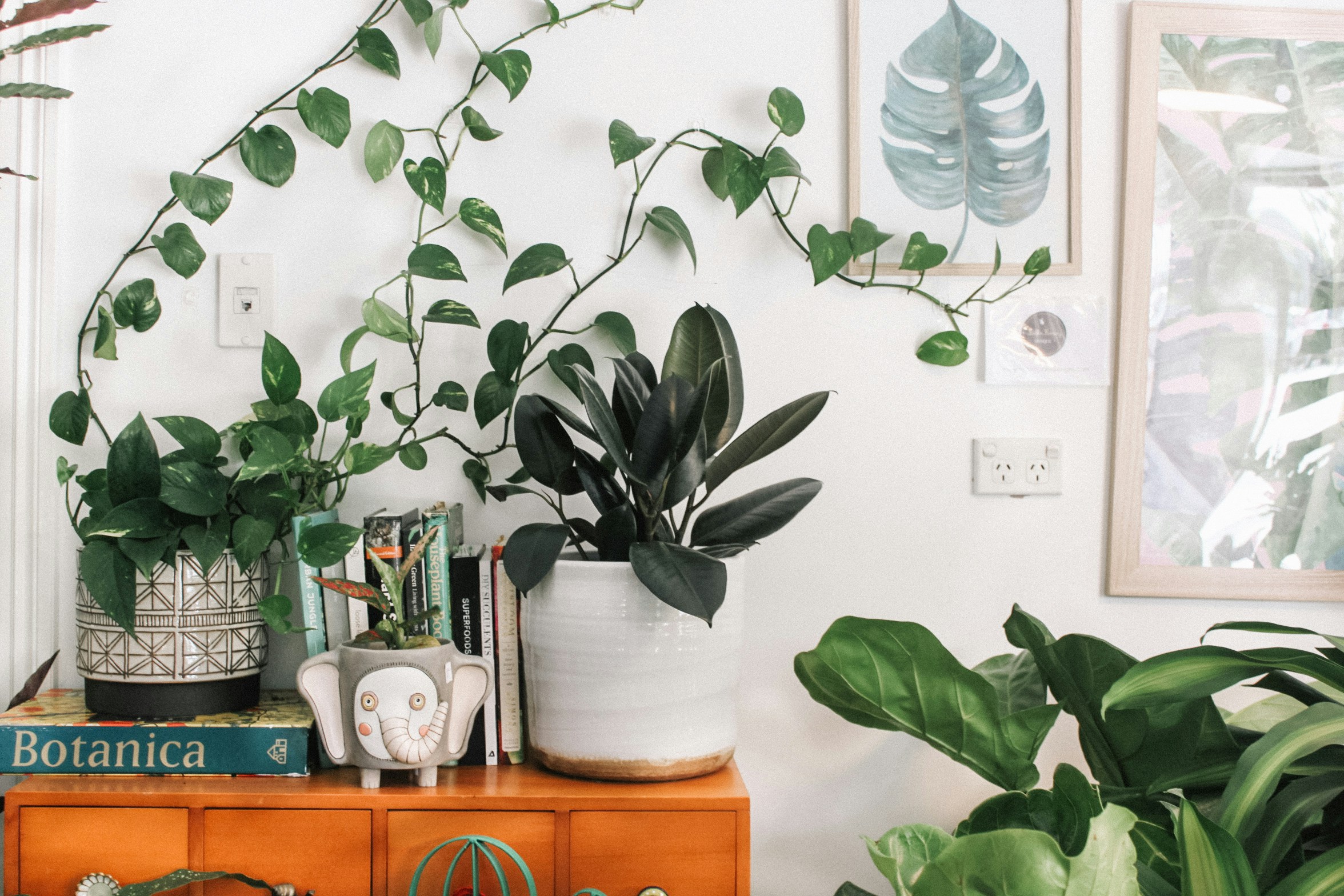
- Integrated Green Spaces: Incorporate plants and natural elements that not only purify the air, but also provide visual respite and reduce stress.
Proven Benefits
Studies have shown that indoor environments that prioritize health can lead to a decrease in sick days, an increase in productivity and, overall, a better quality of life. In addition, these spaces are often more aesthetically appealing, which can increase property value and user satisfaction.
A practical example of healthy design is the implementation of workspaces with adequate rest areas, sound-absorbing materials to reduce ambient noise, and adjustable desks that promote physical activity and reduce the risk of problems related to sedentary lifestyles.
What is an Ecological Interior Design?
Green interior design focuses on creating spaces that are not only sustainable and healthy, but also in harmony with the natural environment. This approach seeks to minimize negative environmental impact by consciously using resources, reducing waste and integrating practices that support the regeneration of local ecosystems.
Definition of Ecological in the Context of Interior Design
Green design goes beyond simply selecting sustainable materials or implementing energy-efficient practices; it is a philosophy that embraces the idea of living in a way that is consistent with the environment. This includes everything from choosing materials and products that are ethically and sustainably sourced to designing spaces that encourage an environmentally friendly lifestyle.
Strategies to Minimize Environmental Impact
Some key strategies for realizing green interior design include:
- Use of Sustainable and Low Impact Materials: Choose materials that are recycled, recyclable, renewable and do not contribute to environmental degradation. This may include wood from sustainably managed forests, bamboo, cork, and natural or recycled textiles.
- Resource Efficiency: Design water and energy systems that maximize efficiency and minimize waste. This may include installing low-flow faucets, gray water recycling systems, and solar panels.
- Biophilic Design: Integrate natural elements directly into the interior design to enhance the occupants' connection to nature. This includes not only plants, but also the use of water, natural light, and materials that mimic natural patterns and textures.
- Electromagnetic and Chemical Pollution Reduction: Minimize the use of electronic devices that emit electromagnetic fields and opt for products with certifications that guarantee low emissions of volatile organic compounds and other harmful substances.
Benefits of Adopting a Greening Approach
Adopting a green approach to interior design not only contributes to the preservation of the planet, but also offers tangible benefits to the health and well-being of occupants. Studies have shown that spaces that incorporate natural elements and reduce pollutants have a positive impact on mental and physical health, improving mood, reducing stress and increasing productivity and creativity.
An exemplary case study could be a residential building that integrates advanced water management systems and uses local, environmentally friendly building materials. This type of project not only demonstrates a commitment to environmental sustainability, but also sets an industry standard for future construction.
Comparison: Sustainable vs. healthy vs. ecological
Although the terms sustainable, healthy and green are often used interchangeably in the context of interior design, each encompasses a distinct philosophy with specific goals and methods. Understanding the differences between these approaches is not only crucial for design professionals, but also for consumers who want to make informed decisions about how to configure their living and working spaces.
Comparison Table Highlighting Key Differences
| Criteria | Sustainable | Healthy | Ecological |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main Objective | Minimize environmental impact and resource use. | Improve the health and well-being of occupants. | Coexist harmoniously with the natural environment. |
| Materials Used | Recycled, renewable, local. | Low VOC, ergonomic, natural. | Sustainable, low impact, biodegradable. |
| Energy Efficiency | High priority. | Considered for comfort. | Essential, integrated with clean technologies. |
| Air Quality | Importantly, use low-impact materials. | Critical, use purifiers and non-toxic materials. | Natural, promotes natural ventilation and biofiltration. |
| Long-term impact | Carbon footprint reduction. | Prevention of environment-related diseases. | Preservation of ecosystems and biodiversity. |
Case Studies or Practical Examples
Sustainable: A practical example of sustainable design can be the use of FSC-certified wood in all carpentry elements, combined with energy-efficient LED lighting, which not only reduces the use of resources but also minimizes the energy demand of the space.
Healthy: In a case of healthy design, an office building incorporates a wide range of indoor plants to improve air quality and large windows that provide abundant natural light, reducing the need for artificial lighting and improving the emotional well-being of employees.
Ecological: An outstanding ecological project could be a residence that uses a rainwater harvesting system, adobe walls that naturally regulate the temperature and a green roof that contributes to local biodiversity and improves the building's thermal insulation.
Reflection
While sustainable design focuses on efficiency and the reduction of negative impacts, healthy design seeks to create an optimal environment for occupants, and green design aims for complete integration with nature. These approaches, while distinct, are complementary and essentially directed toward a more conscious and responsible future. Adopting any of these methods contributes to a significant improvement of the built environment and, by extension, the quality of life and the planet.
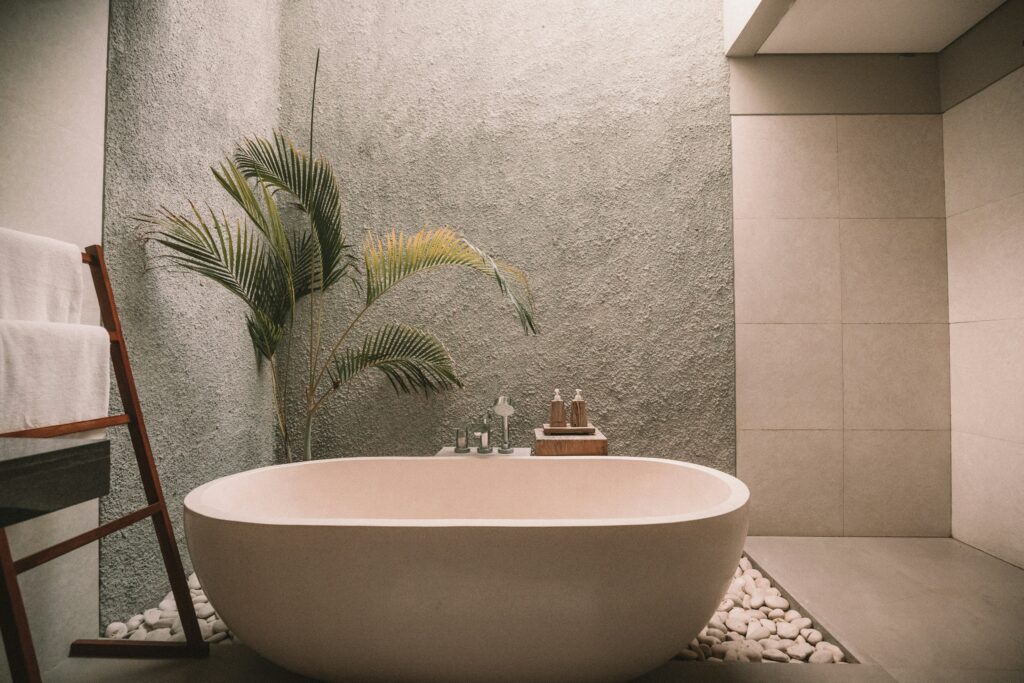

Implementing concepts in real projects
Adopting sustainable, healthy and green design principles is not just a statement of intent, but a practice that requires knowledge, creativity and commitment. Implementing these concepts in real projects may seem challenging at first, but with the right tools and resources, any space can be transformed into a model of sustainability and wellness.
Tips for Applying These Principles in Your Home or Business
1. Needs Assessment and Objectives: Before beginning any project, it is crucial to define what you want to achieve. Are you looking to improve energy efficiency, air quality or integration with the natural environment? Establishing clear objectives from the outset will guide all design decisions.
Material Selection: Choose materials that align with the principles of sustainability (recycled, local, low impact), health (low VOC, natural) and ecology (sustainable, biodegradable). Consult certifications and product recommendations to ensure their provenance and environmental impact.
3. Intelligent Design: Uses design techniques that maximize available natural resources, such as orienting windows to take advantage of sunlight, and incorporating both indoor and outdoor vegetation to improve air quality and aesthetics.
4. Green Technology: Invest in technologies that support your design goals, such as smart thermostats, rainwater harvesting systems and solar panels. These technologies not only reduce resource consumption, but can also offer long-term cost savings.
5. Hiring Professionals: When necessary, seek the help of designers and architects who have experience in the type of project you wish to undertake. Their experience can be invaluable in navigating technical and bureaucratic challenges. Tell me about your project, I'll be happy to help.
examples of sustainable, healthy and environmentally friendly interiors
- The Edge, Amsterdam, The Netherlands:
- Description: The Edge in Amsterdam is considered one of the greenest office buildings in the world. Designed by PLP Architecture, this building uses an advanced building management system that allows users to customize their work environment through an app, thus optimizing energy consumption and improving comfort.
- Principles Applied: Sustainability (uses solar energy and has one of the highest BREEAM scores), Health (maximizes natural light and uses a ventilation system that improves indoor air quality), Green (minimizes its carbon footprint and encourages sustainable transportation with ample facilities for bicycles and electric cars).
- Bullitt Center, Seattle, United States:
- Description: Known as the world's greenest commercial building, the Bullitt Center operates completely without energy waste and strives to exceed the requirements of the Living Building Challenge.
- Principles Applied: Sustainable (generates its own solar energy and treats all water on site), Healthy (uses non-toxic materials and promotes a design that encourages movement, such as "irresistible stairs"), Ecological (designed to mimic the functions of a natural ecosystem).
- Pixel Building, Melbourne, Australia:
- Description: This office building is not only aesthetically innovative, it is also one of the first to achieve a zero carbon footprint in Australia.
- Principles Applied: Sustainable (uses solar panels and rainwater harvesting systems), Healthy (incorporates a biophilic design that includes ample indoor and outdoor green spaces), Ecological (uses recycled materials and construction techniques that minimize environmental impact).
- One Angel Square, Manchester, United Kingdom:
- Description: The Co-operative Group's headquarters is one of the highest environmentally rated office buildings in the world according to BREEAM, with a design that emphasizes energy efficiency and sustainability.
- Principles Applied: Sustainable (uses thermal energy from the ground and rainwater harvesting), Healthy (maximizes natural light and improves indoor air quality with low-emission materials), Ecological (uses local and recycled materials, and significantly reduces CO2 emissions).
These projects are outstanding examples of how biointeriorism can be successfully implemented in different contexts and climates, showing the way to a more sustainable and healthy future in interior design.
Conclusions
Throughout this article, we have explored in depth the concepts of sustainable, healthy and green design, demystifying these terms and providing clear examples of their application in the world of interior design. These approaches are not simply passing trends; they represent crucial movements toward a future where spaces are not only aesthetically pleasing, but also environmentally responsible and promoters of human health.
Adopting these design principles offers significant benefits: they reduce the environmental impact of buildings, improve the quality of life for occupants, and promote long-term sustainability. Each approach, while distinct, contributes to a common goal: the creation of spaces that respect both people and the planet.
It is imperative that designers and consumers alike continue to promote and adopt these practices. In doing so, they will not only transform the spaces in which they live and work, but also support the global fight against climate change and environmental degradation.
This call to action is clear: let's integrate sustainability, health and ecology into our interior design projects to pass on a better world to future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How does sustainable design differ from green design?
A: Although both terms are often used interchangeably, sustainable design focuses primarily on minimizing environmental impact and using resources efficiently so as not to compromise the capacity of future generations. Ecological design, on the other hand, seeks a complete and harmonious integration with the natural environment, prioritizing biodiversity and ecosystem conservation.
How can I verify that the materials I use are really sustainable or healthy?
A: Look for third-party certifications such as the FSC seal for wood, Energy Star for appliances, or GREENGUARD for products with low impact on indoor air quality. These certifications ensure that products meet specific sustainability and health standards.
Is it more expensive to implement sustainable, healthy or eco-friendly interior design?
A: Initially, it can be more expensive due to the investment in high quality materials and advanced technology. However, these costs are often offset in the long run by savings in energy, water, and maintenance, as well as potential health benefits that reduce medical expenses.
What simple steps can I take to make my home more sustainable without a complete renovation?
A: Small changes such as installing LED light bulbs, using programmable thermostats, choosing low-VOC paints and finishes, and adding insulation to your home can make a big difference. Also consider incorporating plants to improve indoor air quality.
Can I apply these design principles in a small or rented space?
A: Absolutely, the size of your space does not limit your ability to implement sustainable, healthy and eco-friendly principles. You can opt for furniture made from sustainable materials, use decorations that improve environmental quality, and invest in energy-efficient products that you can take with you if you move.